Novel Strategy to Synthesize Low-molecular-weight and High Trans-1,4 Polyisoprene
Synthetic rubber especially low-molecular-weight and high trans-1,4 polyisoprene liquid rubber have been widely applied. At present, cationic polymerization is the dominant way to prepare high trans-1,4 polyisoprene.However, it faces the challenge of uncontrolled cyclization or branching side reactions. It's important to develop highly effective cationic polymerization system to produce high trans-1,4 polyisoprene liquid rubber with high double bond content.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WANG Qinggang from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a novel strategy of protonic acid and ionic liquid catalysis to synthesize low-molecular-weight and high trans-1,4 polyisoprene.
The synergistic effect of Tf2NH and ionic liquid including Tf2N- counter anion performed well, affording high yield (> 99%) and high double bond content (up to 99%) simultaneously.
Mechanistic investigation indicated that a weak interaction between the double bonds and bulky cations could reduce the elctrondensity of double bonds in polyisoprene to prevent the undesired "re-protonation". Furthermore, high performance can still be maintained after ionic liquid was recycled for five rounds.
The above advantages provide a feasible green pathway for the industrial production of high trans-1,4 polyisoprene liquid rubber.
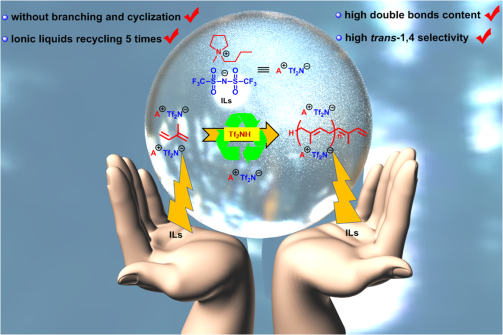
High trans-1,4 polyisoprene liquid rubber polymerization. (Image by ZHU Guangqian and WANG Liang)
(Text by ZHU Guangqian and WANG Liang)
Contact:
CHENG Jing
Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Tel: 86-532-80662647/80662622
E-mail: chengjing@qibebt.ac.cn
