Scientists Developed Multiple Sulfide Solid Electrolyte and Excellent Solid-state Batteries
All-solid-state (sulfide) battery is a cutting-edge technology which promotes the progress of society and human. It has several advantages such as high safety, high energy density, high temperature resistance and long life comparing. It can solve a series of problems of traditional organic electrolyte batteries.
At present, new energy vehicles urgently need to improve cruising range and safety. In response to this demand, leading companies, such as Japan's Toyota, Samsung, BMW, etc., are actively developing technology layout on solid-state batteries. So far, all-solid-state batteries worldwide are in the technical stage of research and development to pilot test.
A research team led by Prof. WU Jianfei from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have been successfully developed a series of sulfide solid electrolytes and excellent solid-state batteries.
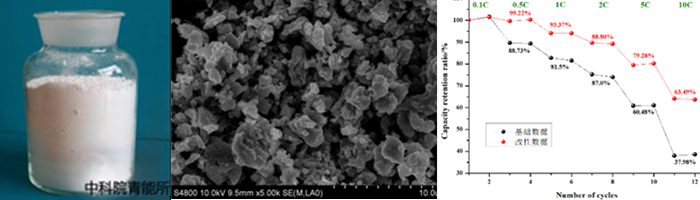
Researchers have developed a variety of sulfide solid electrolytes, including germanium series and halogen series, ionic conductivity of which can reach 10-2~10-4 S cm-1. The solid electrolytes have been put into pilot scale production.
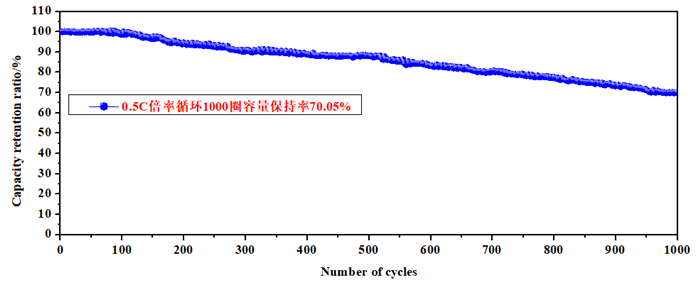
The solid state batteries have excellent cycling and rate performance. The capacity at 25 ℃ can remain 70.05% under 0.5 C after 1000 cycles, and remain 79.28% at a high rate of 5C.
The research group conducted detailed research on the interface between the electrode and the solid electrolyte, and provided theoretical basis and technical guidance for the scale-up production of solid-state batteries.
 、
、
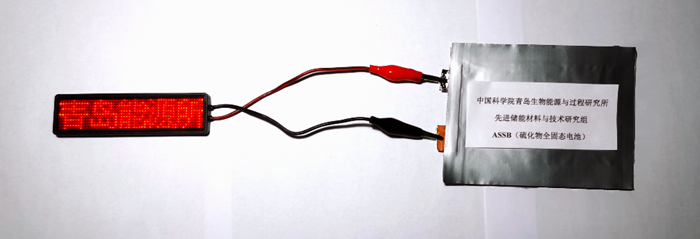
Related Achievements in Sulfide Solid Electrolytes and All-Solid-State Batteries (Image by SUN Xiaolin)
In 2019, the research group signed a cooperation intention with Weichai Power Co., Ltd. to promote the industrialization of sulfide solid-state batteries in new energy vehicles.
The technical cooperation between the research team and Japan was also approved for Shandong Province Key Research and Development Plan in 2019.
This work was supported by Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy (DNL, CAS).
(Text by SUN Xiaolin)
Contact:
CHENG Jing
Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Tel: 86-532-80662647/80662622
E-mail: chengjing@qibebt.ac.cn