A Novel Nanocomposite Used to Modify Separators of Lithium-sulfur Batteries
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have been regarded as a promising substitute to the current lithium-ion batteries. They have high energy density, five times higher than that of the state-of-the-art lithium-ion batteries. In addition, Li-S batteries centralize the advantages of environmental benignity and low cost.
However, the electrochemical performances of Li-S batteries are seriously compromised by the polysulfide (LiPS) shuttling during charge and discharge process. The LiPS dissolves into the electrolyte, given a loss of active materials, and thus a decay of cycle performance for Li-S batteries.
To solve the problems above, the Advanced Energy Storage Materials and Technology Group from Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a novel nanocomposite for the modified separator of Li-S batteries.
They used transition metal compound CoNi1/3Fe2O4 (CNFO) nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes (CNT) as functional interlayer. Benefiting from the strong adsorption of CNFO and high conductivity of CNT, the Li-S batteries exhibited an excellent discharge capacity as high as 897 mAh g-1 at 2.0 C and maintained 84% after 250 cycles. Meanwhile, a reversible specific capacity of 869 mAh g-1 at 0.5 C with high Coulombic efficiency could be also obtained over 100 cycles at an elevated temperature (60 °C). The functional interlayer greatly inhibited the LiPS shuttling and boosted the electrochemical performance of Li–S batteries.
The relevant work was published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, and generous supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21673267) and DICP&QIBEBT (UN201702).
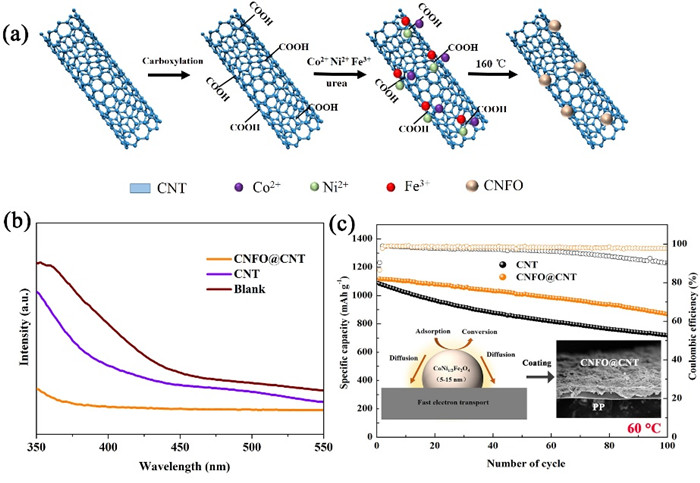
Figure 1 (a) Schematic illustration of CNFO@CNT nanocomposite preparation. (b) UV-vis spectra of CNFO@CNT nanocomposite. (c) Cycle performance of Li-S batteries under 60°C. (Image by LIU Tao)
(Text by Sun Shimei)
Contact:
CHENG Jing
Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Tel: 86-532-80662647
E-mail: chengjing@qibebt.ac.cn