QIBEBT Developed Novel Peptide Microarray with High Performance for Cellulase
The peptide microarray received much attention from all research fields due to its excellent properties, such as small size, affordability, convenience, high-throughput, automation and speediness. However, to date, the performance of peptide microarray has been limited by the composition, direction and density of peptide ligands used.
To respond to these challenges, the researchers from the Laboratory for Biosensing, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy & Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) took the cellulytic enzyme endoglucanase I (EG I) as a model for selection of its specific peptide ligands from the f8/8 landscape library. One peptide EGSDPRMV was obtained, which could bind EG I specifically with highest affinity. Subsequently, the peptide EGSDPRMV mediated by symmetrical carrier Ff phage, was used to construct peptide microarray. This work was published online in Analytical Chemistry (Analytical Chemistry2014, Article ASAP, DOI:10.1021/ac501265y).
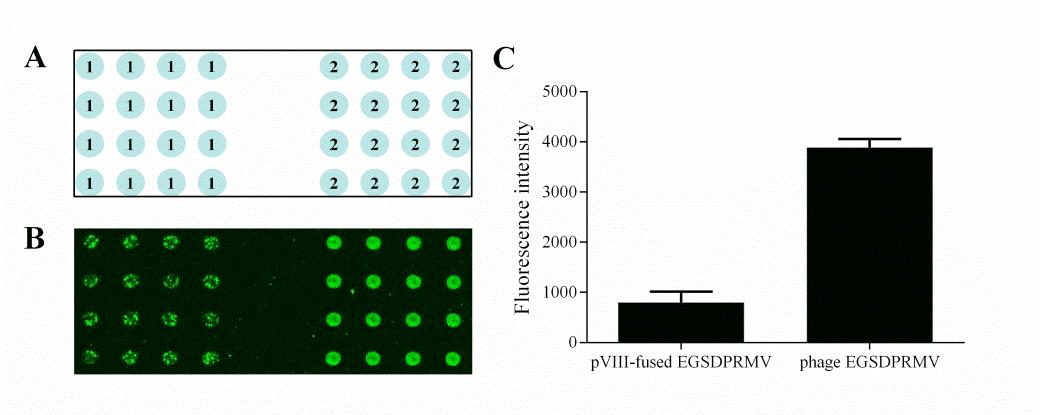
As shown in Figure 1, the fluorescent signal of the phage EGSDPRMV-mediated peptide microarray was more reproducible and about four times higher than the value for the major coat protein, pVIII-fused EGSDPRMV-based microarray. This result suggested a high efficiency of the proposed phage EGSDPRMV-mediated peptide immobilization method. Further, the peptide microarray based symmetrical carrier Ff phage also demonstrated good sensitivity and reproducibility. This peptide microarray would bring new opportunity in cellulase-related bioenergy research.
This research was led by Prof. LIU Aihua from the Laboratory for Biosensing, QIBEBT. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and CAS135 Program, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Figure 1. (A), Patterns of fabricated microarray, in which 1 indicated the pVIII-fused EGSDPRMV and 2 indicated phage EGSDPRMV; (B), The image of peptide microarray incubated with Cy3 labeled EG I (100 nM); (C), The quantitative results of image B. (Image by Laboratory for Biosensing, QIBEBT)
Contact:
Prof. LIU Aihua
Email: liuah (AT) qibebt.ac.cn
Web: http://english.qibebt.cas.cn